Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
Software Defined Networking (SDN) is a relatively new concept. It allows networks to be defined and controlled using software external to the physical networking devices.
With SDN, a relatively simple physical network can be programmed to act as a complex virtual network. It can become a hierarchical, complex and secured virtual structure that can easily be changed without touching the physical network components.
An SDN can be controlled from a single management console and open APIs can be used to manage the network using third party software. This is particularly useful in a cloud environment, where networks change frequently as machines are added or removed from a tenant’s environment. With a single click of a button or a single API call, complex networks can be created within seconds.
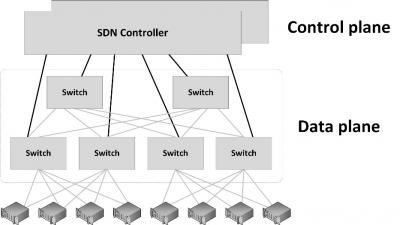
SDN works by decoupling the control plane and data plane from each other, such that the control plane resides centrally and the data plane (the physical switches) remain distributed, as shown in the next figure.
In a traditional switch or router, the network device dynamically learns packet forwarding rules and stores them in each device as ARP or routing tables. In an SDN, the distributed data plane devices are forwarding network packets based on ARP or routing rules that are loaded into the devices by an SDN controller devices in the central control plane. This allows the physical devices to be much simpler and more cost effective.
Network Function Virtualization
In addition to SDN, Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is a way to virtualize networking devices like firewalls, VPN gateways and load balancers. Instead of having hardware appliances for each network function, in NFV, these appliances are implemented by virtual machines running applications that perform the network functions.
Using APIs, NFV virtual appliances can be created and configured dynamically and on-demand, leading to a flexible network configuration. It allows, for instance, to deploy a new firewall as part of a script that creates a number of connected virtual machines in a cloud environment.
This entry was posted on Friday 23 September 2016
 English
English